Show HN: Survey on AI Agents in Production (324 Respondents)
AI Agents: Unlocking Potential Across Industries
Chapter 1: Defining AI Agents
AI agents are not static models but systems that can autonomously plan, adapt, and refine their behavior based on goals and real-time feedback.
- Autonomy: AI agents can operate with minimal human intervention.
- Goal-Oriented Reasoning: Agents work towards specific objectives, using AI-driven logic to achieve those goals.
- Contextual Awareness: The best agents integrate contextual or domain-specific knowledge, filtering out noise and focusing on relevant signals.
- Safety & Interpretability: Robust safety mechanisms and transparency in decision-making are essential. AI agents should be designed to minimize harmful or biased outputs and make it easy to trace decisions.
AI agents offer more than just automated chatbots. They can handle tasks that once demanded human judgment and domain knowledge.
Chapter 2: Drivers of AI Agent Adoption
A YouGot.us survey in November 2024 revealed a diverse group of practitioners driving AI agent adoption, from startups to large enterprises.
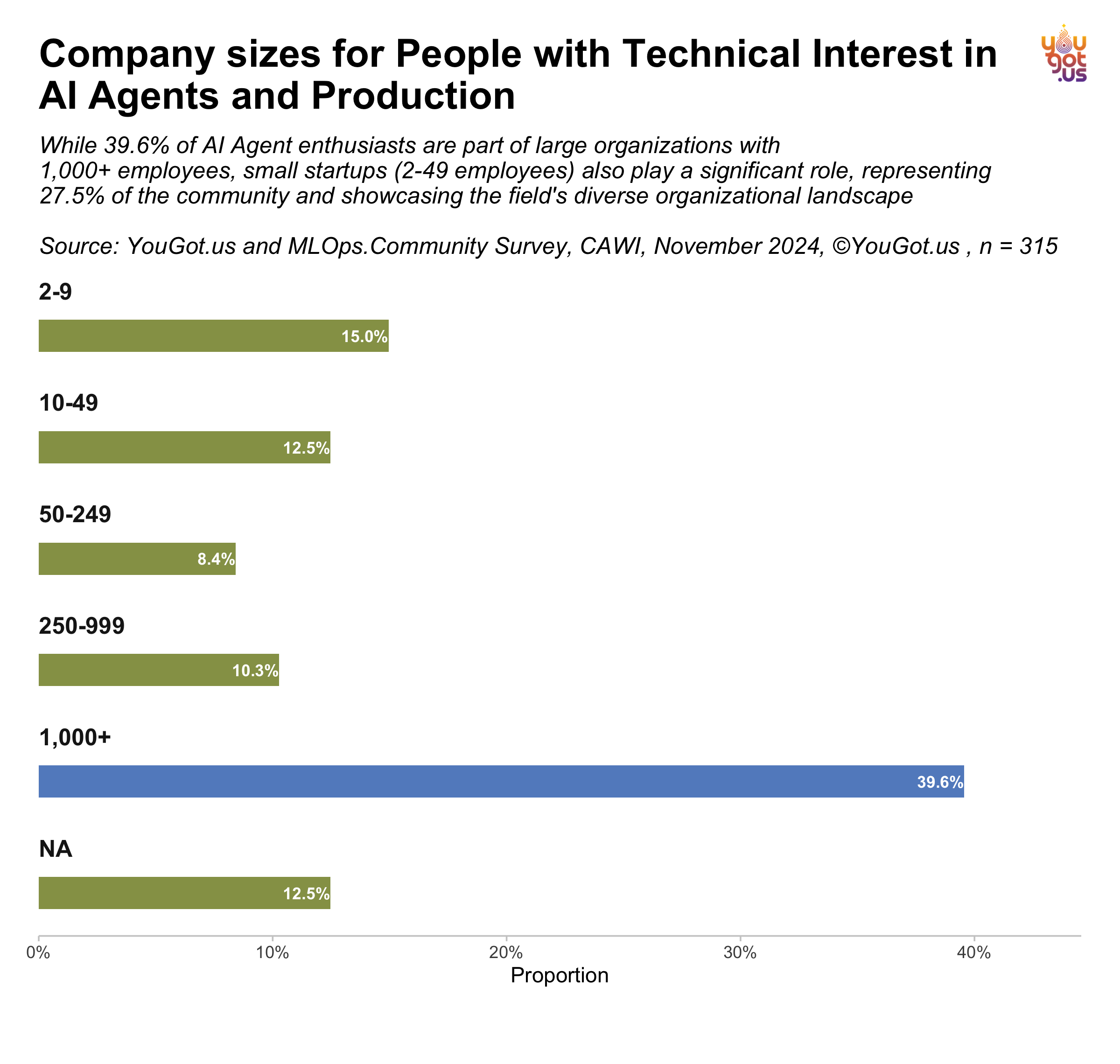
Company Sizes Represented:
- 27.5% from small startups (2-49 employees)
- 39.6% from organizations with 1,000+ employees
Roles Behind AI Agents:
- AI/ML Engineers: 17.9%
- Software Engineers: 15.1%
How Roles Vary by Company Size:
- Data scientists primarily work in larger enterprises.
- CTOs and DevOps engineers are common in smaller companies.
- Software engineers, AI/ML engineers, and product managers are evenly distributed across mid-sized companies.
Leading AI Agent Industries:
- Technology: 43%
- Finance: 10.3%
- Retail and E-Commerce: 10%
- Healthcare: 6.5%
Chapter 3: The Current State of AI Agent Adoption
While AI agents are generating buzz, our survey reveals that extensive deployments remain limited.
Adoption Rates:
- 21.8% report no adoption
- 29.0% report limited adoption
- 24.3% report moderate adoption
- 10.9% report extensive adoption
- 5.0% report full integration
Early-Stage Startups vs. Enterprises:
Early-stage startups (50%) are more likely to achieve full AI agent integration than established enterprises (6%).
Reasons for Adoption:
- Improving operational efficiency (47.4%)
- Automating repetitive tasks (35.5%)
- Enhancing customer experience (29.9%)
- Innovating products and services (23.4%)
- Gaining competitive advantage (27.4%)
Chapter 4: Key Use Cases and 2025 Focus Areas
Current Usage:
- Internal knowledge management
- Customer support
- Coding assistance
Looking Ahead:
Organizations are planning to expand AI agent use to:
- Process Optimization & Automation
- Human Resources & Employee Support
- Marketing Automation & Lead Generation
Divergent Approaches:
Early-stage startups prioritize marketing automation and project management, while larger enterprises focus on personal productivity and content creation, reflecting different risk tolerance levels.
Key Takeaways:
- Coding assistance and internal knowledge management are successful use cases.
- A hybrid of AI and human agents is effective for customer support.
- Startups and enterprises differ in their use case priorities.